Technology >> Photocatalyst >> Introduction |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| What's Photocatalyst | |||
 |
|||
| Photocatalyst is the acceleration of a photoreaction in the presence of a catalyst. There are many materials to be photocatalyst such as TiO2, ZnO, SnO2, Cds, ZnS, GaP,..etc. due to high stability, excellent redox ability, and environmental friendly, Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) is the most popular material. | |||
 |
|||
| Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) is an n-type semiconductor with band gap energy of 3.2eV. When Nano photocatalyst titanium dioxide(TiO2) absorbs Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or illuminated light source (fluorescent lamps), it will produce pairs of electrons and holes. The electron of the valence band of titanium dioxide becomes excited when illuminated by light. The excess energy of this excited electron promoted the electron to the conduction band of titanium dioxide therefore creating the negative electron(e-) and positive-hole(h+) pair. | |||
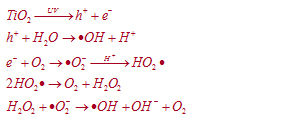 |
|||
| The positive-hole of titanium dioxide breaks apart the water molecule to form hydrogen gas and hydroxyl radical. The negative electron reacts with oxygen molecule to form super oxide anion. These reaction oxygen species (ROS) can damage the structure and disrupt the biochemistry of bacteria and virus-infected cells. In the presence of the hydroxyl radical and molecular oxygen, organic compounds are oxidized ultimately to carbon dioxide and water. This cycle continues when light is available. | |||
 |
|||