技術 >> 荷葉疏水奈米塗料 >> 荷葉效應 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
荷葉效應 | |||
 |
||||
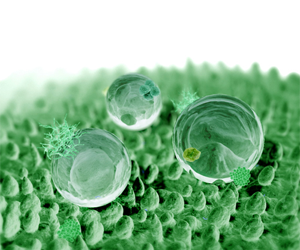
| 荷葉具有疏水自潔的特性廣為人們所知,當外來的污染物(如灰塵、油脂類等)接觸到荷葉表面時,污染物無法沾在荷葉表面上,當遇到水時會形成水珠,只要葉面有一個很小的傾斜角,水珠即可以將污染物帶走,一般稱為荷葉效應(Lotus Effect)。 |
||||
| Analysis of lotus leaves by Scanning Electron Microcopy (SEM) reveal that the leaves surface is composed by hierarchical double structure (micro-nano size). This hierarchical double structure is formed out of a characteristic epidermis and the covering waxes. | ||||
 |
||||
| The epidermis of the lotus plant possesses papillae with 10 to 20 µm in height and 10 to 15 µm in width and plenty of nano structure tubules on the surface of papillae. Water droplets interfacing with the leaf are in contact with a large fraction of air. This forces the water to roll off and dirt particles on the leaf surface to picked up by water droplets. | ||||